Music publishing is about promoting and monetizing musical compositions. It’s a critical process that ensures songwriters and composers receive appropriate royalties and opportunities for their work.
This segment of the music industry, one of its oldest, predates even the earliest recording mediums, highlighting its longstanding importance. As technology advanced, the scope of publishing expanded to include the management of rights in various formats, from vinyl records to digital streams.
This historical progression underscores the adaptability and enduring relevance of music publishing in the ever-changing music industry. Today, publishing encompasses a wide range of activities.
Publishers are responsible for promoting compositions, securing opportunities for their use, and collecting royalties on behalf of the songwriters. This role has become increasingly complex in the digital age, where music consumption spans various platforms and formats.
There are Different Types of Copyrights
Understanding the different types of copyrights is essential to grasp the full scope of publishing rights. There are two main types of copyrights in music: composition rights and master recording rights.
Composition Copyrights
Composition copyrights protect the rights of the songwriter or composer. This includes the melody, lyrics, and arrangement of a song. The holder of the composition copyright has the exclusive right to use, reproduce, and distribute the work.
Master Recording Copyrights
Master recording copyrights, on the other hand, protect the rights of the recording artist or the record label. This type of copyright pertains to the actual recorded version of a song. It grants the holder control over the reproduction, distribution, and commercial use of that specific recording.
What Are Publishing Royalties?
Music publishing royalties are the payments songwriters and composers receive when their compositions are used commercially. There are three main types of music publishing royalties: Mechanical Royalties, Public Performance Royalties, and Synchronization License Fees.
Mechanical Royalties
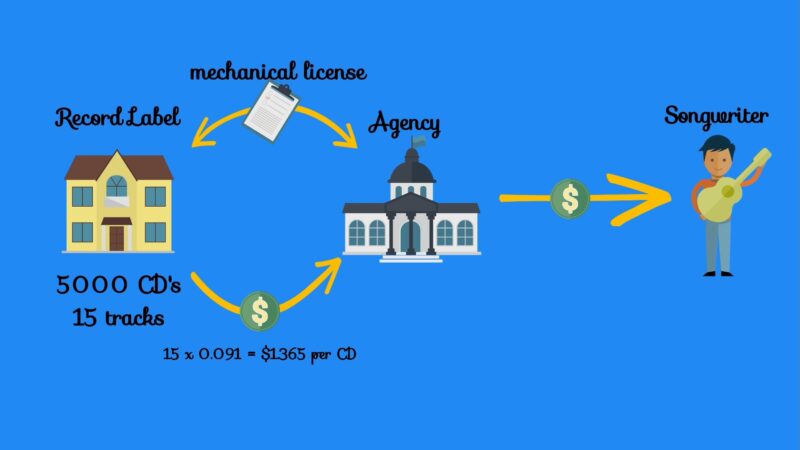
Mechanical royalties are generated when a musical composition is reproduced. In the past, this primarily involved the physical reproduction of music, like CDs or vinyl records.
Today, it largely comes from digital reproductions, such as streaming services. On the other side, some records stores manages to survive the digital era, especially because there are still many enthusiasts that prefer using old-school music formats. One of the best examples is Josey Records.
Public Performance Royalties
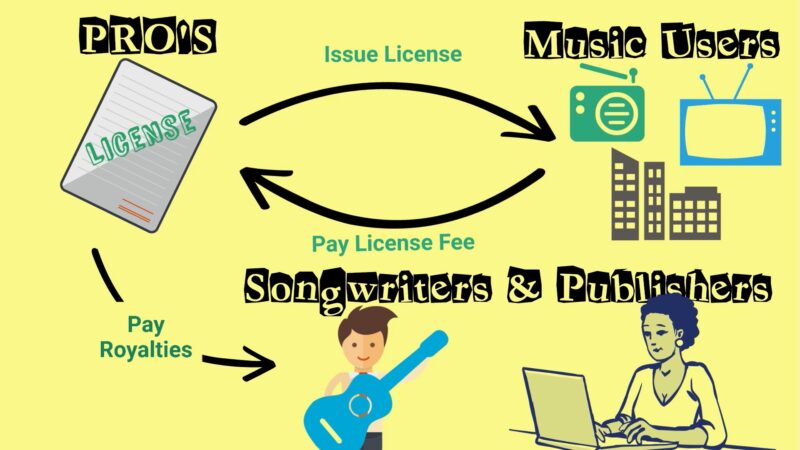
Public Performance Royalties are earned when a composition is played in public. This includes live performances, radio broadcasts, and background music in public spaces. Performance Rights Organizations (PROs) collect these royalties and distribute them to the rightful owners.
The Role of Publishers

The publishers play essential role in the industry. They are responsible for several key functions, including the administration, registration, collection, and audit of royalties. Their role extends beyond mere administration, encompassing talent scouting and negotiation of music rights.
Administration and Royalty Collection
The publishers administer the rights of compositions, ensuring that royalties are correctly collected and distributed. This involves registering works with various organizations, tracking usage, and conducting audits to guarantee accurate royalty payments.
Talent Scouting and Rights Negotiation
Publishers also engage in scouting for new talent, particularly focusing on songwriters who write for other artists. They negotiate music rights on behalf of their clients, especially in complex arrangements involving multiple songwriters or sampling.
International Royalties and Global Publishing
The global nature of the music industry means that songwriters need to navigate a complex web of international royalties. To fully capitalize on their work, songwriters must register with multiple organizations worldwide.
The Challenge of International Royalties
Collecting international royalties presents a unique challenge. Different countries have different systems and laws governing the royalties. Songwriters and publishers must understand these nuances to ensure they receive all due royalties.
The Role of Publishers in International Royalties
They play a crucial role in managing international royalties. They help songwriters register with the appropriate organizations globally and ensure that royalties from different countries are accurately collected and distributed.
More About the Financial Terms
The publishing rights have a significant economic impact on the music industry. According to the International Confederation of Societies of Authors and Composers (CISAC), in 2019, global collections for creators totaled €9.6 billion, with a substantial portion coming from publishing rights. This revenue stream is vital for songwriters, who often rely on royalties as their primary source of income.
Real-World Examples
For instance, the American Society of Composers, Authors and Publishers (ASCAP) and Broadcast Music, Inc. (BMI), two of the largest performance rights organizations in the United States, collectively distribute billions of dollars in royalties to their members annually. In 2019, ASCAP collected over $1.274 billion in licensing fees and distributed more than $1.184 billion in royalties, while BMI collected $1.311 billion and distributed $1.233 billion.
The Importance of Royalties
These royalties are crucial for songwriters, especially in an era where income from record sales has diminished due to the rise of streaming services. For example, mechanical royalties from streaming services like Spotify or Apple Music have become a significant source of income.
In 2020, digital music streaming accounted for nearly 80% of all music industry revenues in the United States, as reported by the Recording Industry Association of America (RIAA).
Why Are Record Labels Important?

Music publishers and popular labels provide expertise in administering rights, collecting royalties, and securing opportunities for compositions. They have established networks and resources that individual artists typically do not possess.
For example, negotiating synchronization licenses for TV, movies, or advertisements is an area where publishers can significantly benefit artists.
Should Artists Avoid Them?
The only way to gain full control over the rights for your tracks is by choosing self-publishing. However, it requires a deep understanding of the music industry, including rights management, royalty collection, and business networking.
For many artists, especially those without industry experience, this can be a very difficult process. On the other hand, large labels have enough resources and connections to help an artist to quickly gain more attention.
On the other hand, there are potential downsides that you could face. Comparing different labels is essential for making the right choice. Here are some things that you should look to avoid:
- Loss of Control: Working with a publisher often means giving up some control over how a song is used.
- Costs: Publishers take a percentage of royalties as compensation for their services.
- Complex Contracts: Contracts with publishers can be complex and may lock artists into long-term agreements.
FAQs
How do music publishers assist with copyright infringement issues?
Music publishers play a crucial role in protecting against copyright infringement. They monitor the use of the compositions they represent and take legal action if a song is used without proper licensing. This includes negotiating settlements or pursuing legal remedies to ensure that the rights of songwriters and composers are respected and that they receive appropriate compensation for unauthorized uses of their work.
Can independent artists benefit from music publishing if they don’t have a large following?
Yes, independent artists can benefit from music publishing even without a large following. Music publishers can help these artists find opportunities to monetize their music, such as securing placements in films, TV shows, or advertisements. Additionally, publishers can manage the collection of royalties from various sources, ensuring that artists are paid for the use of their music, regardless of their fan base size.
How does the rise of user-generated content platforms (like YouTube or TikTok) affect music publishing rights?
The rise of user-generated content platforms has significantly impacted music publishing rights. These platforms have created new avenues for music usage, requiring publishers to adapt by establishing new licensing agreements and royalty collection methods.
Are there any specific challenges in music publishing for genres like classical or jazz?
Yes, genres like classical or jazz face unique challenges in music publishing. These genres often involve complex compositions with multiple rights holders, making royalty distribution more complicated. Additionally, the market for these genres is typically smaller than for mainstream music, requiring publishers to seek niche opportunities for monetization, such as performances, sheet music sales, and specialized recordings.
What role do music publishers play in helping emerging artists develop their careers?
Music publishers can be instrumental in developing the careers of emerging artists. They can provide valuable industry connections, facilitate collaborations, and offer guidance on career decisions. Publishers also help emerging artists gain exposure by securing placements for their music in various media, thereby broadening their audience and enhancing their reputation in the industry.
Summary
Music publishing rights are a critical component of the music industry, providing financial stability and creative opportunities for artists. While navigating these rights can be complex, the benefits of professional music publishing are clear.
As the industry evolves, both artists and publishers must adapt to new challenges and opportunities, ensuring that the creation of music remains a viable and rewarding pursuit.
